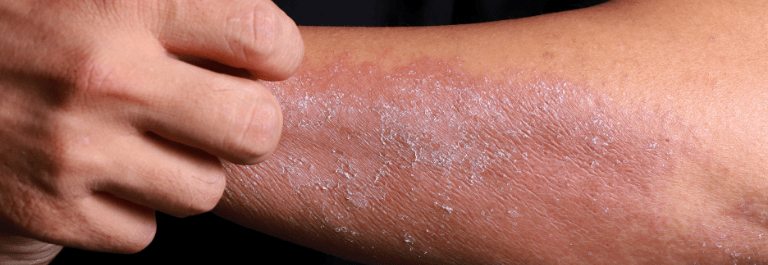
If you’ve noticed peeling skin as part of your eczema, you’re definitely not alone. Many people with atopic dermatitis experience redness, scaling, and skin peeling during flare-ups. Most of the time, this peeling is mild, but in rare cases, it can be a sign of something more serious, like exfoliative dermatitis.
Knowing the difference between everyday eczema symptoms and when it’s time to see a doctor is important. Let’s break it down.
What is Exfoliative Dermatitis?
Exfoliative dermatitis (dermatitis exfoliativa) is a rare but potentially life-threatening skin condition. It causes widespread skin peeling and redness, sometimes affecting more than 90% of the body.
It can be triggered by:
-
Preexisting conditions like psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or contact dermatitis
-
Drug reactions (to steroids, antibiotics, chemotherapy, etc.)
-
Underlying cancers such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
-
Rare skin disorders like pityriasis rubra pilaris
-
Or sometimes, no clear cause at all
Because of its severity, exfoliative dermatitis always requires prompt medical care. Doctors will usually run tests, review your history, and sometimes admit patients to the hospital for close monitoring.
Why is My Eczema Peeling?
In atopic dermatitis, the skin barrier loses its body’s ability to hold in moisture, causing dryness, scaling, and peeling. But in exfoliative dermatitis, the turnover of skin cells accelerates abnormally. Instead of renewing every few weeks, cells shed too rapidly, leaving affected skin raw and vulnerable.
This process can:
-
Lead to serious complications such as dehydration, electrolyte balance disturbances, or secondary infection
-
Cause hair loss, heat loss, and in some cases even heart failure or cardiac failure
-
Affect the mucous membranes, resulting in discomfort and higher infection risk
-
Trigger post inflammatory hyperpigmentation or, rarely, keloid formation after healing
Some patients may also develop complications like red man syndrome, widespread infection, or fluid loss, making hospital-level care necessary.
Symptoms and Risks of Exfoliative Dermatitis
-
Peeling skin across large areas of the body
-
Redness, erythema, and scaling
-
Itching and burning sensations
-
Hair loss or brittle nails
-
Chills, fever, and fluid imbalance
-
Risk of complications including antibiotic-resistant infection and cancer-related triggers
Because it is a life threatening condition, it is important to treat exfoliative dermatitis with medical supervision.
How Do Doctors Treat Exfoliative Dermatitis?
If exfoliative dermatitis is suspected, immediate medical attention is required. Hospital admission is common, as patients may develop complications quickly.
Appropriate treatment may include:
-
Bed rest and careful monitoring
-
Eczema cream and bland emollients to hydrate the skin and restore barrier functionBland emollients to hydrate the skin and restore barrier function
-
Wound care for open or fragile areas
-
Oral antihistamines to reduce itch and improve comfort
-
Antibiotics if secondary infection is present
-
Management of electrolyte balance and fluid loss
-
Avoiding potential triggers such as irritating medications or harsh products
-
Long-term follow up to prevent recurrence
Your doctor will assess your clinical findings and medical history to determine the underlying cause and recommend the right treatment plan.
Natural Ways to Soothe Peeling Eczema Skin
For those dealing with mild skin issues from atopic dermatitis, natural remedies can help soothe peeling skin and improve the appearance of affected skin. These are not substitutes for hospital care in cases of exfoliative dermatitis, but they may help manage everyday eczema dryness and irritation:
Organic Calendula Oil
Rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and plant compounds, calendula oil helps moisturize and calm affected skin. It’s safe for babies and adults, and can be applied directly to peeling areas or added to bath water for an extra boost of hydration.
20% Pine Tar Soap with Tallow
This natural eczema soap helps slow rapid skin cell turnover and restore the appearance of rough, peeling skin. It also has anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory benefits, making it helpful for eczema, dandruff, psoriasis, and even scalp seborrheic dermatitis.
Super Dry Soother
Formulated with certified safe herbs, this balm is designed for scaly, peeling skin. It supports healing from sunburn, windburn, and chronic eczema dryness, while reducing the risk of irritation.
Nourish + Hydrate Manuka Balm
This rich, soothing balm is powered by manuka honey and a blend of five other natural ingredients to deeply hydrate and calm peeling, scaly, and itchy skin. Gentle, non-stinging, and ultra-nourishing, it’s ideal for sensitive skin conditions like eczema and for post-flare wound care when your skin needs extra comfort and repair.
Remedywear™ Sleeves & Bandages (Babies to Adults)
Made with breathable TENCEL embedded with zinc oxide, these sleeves are ideal for wet wrap therapy or for protecting affected skin from scratching. They help speed up recovery, reduce irritation, and can be worn under clothing day or night.
When to See a Doctor
If your peeling eczema skin is spreading, linked to generalized exfoliative dermatitis, or accompanied by serious complications such as fever, infection, or severe redness, it’s important to consult with your doctor or healthcare providers immediately. Dermatitis exfoliativa may require hospitalization, antibiotics, fluid management, wound care, and close follow-up.
Remember: While natural remedies like calendula oil, manuka cream, beef tallow cream, pine tar soap, and Remedywear sleeves can soothe symptoms and improve your skin's appearance, they are not a replacement for appropriate treatment when life-threatening complications are a risk.