Q: My skin is red, itchy, and irritated. How do I know if it’s eczema instead of fungal infection?
A: Great question! Many people confuse eczema with fungal skin infections because both can cause redness, itchy rashes, and irritation. But while eczema is a chronic skin condition, fungal infections are usually caused by fungi that grow in moist areas of the body and can be passed through skin to skin contact.
Let’s break it down.
Q: What is Eczema?
A: Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. The most common type is atopic dermatitis, though other forms include nummular dermatitis (coin-shaped lesions), dyshidrotic eczema (blisters on hands/feet), and discoid eczema.
-
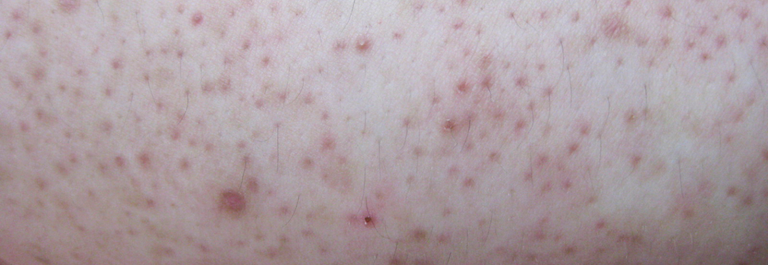
Symptoms: itchy rash, swollen skin, dry patches, and sometimes red rash or scaly lesions.
-
Triggers: environmental factors (pollen, mold, pet fur), certain fabrics, harsh products, stress, or repeated scratching.
-
Is it contagious? No. Eczema is a chronic condition and not spread through contact.
Eczema treatment often includes gentle skincare with mild soap, eczema creams, topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors, bleach baths, and wet wrap therapy. Because it’s a long-term chronic skin condition, treatment focuses on controlling flare ups and preventing secondary infections.
Q: What is a Fungal Infection?
A: It's a skin infections caused by fungi such as candida or dermatophytes. While some fungi live harmlessly on the outer layers of skin, when they multiply excessively, they cause problems.
-
Common types:
-
Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)
-
Tinea capitis (fungal scalp infection)
-
Jock itch (infection in the skin folds of the groin)
-
Candida yeast infections in warm, damp affected areas like the diaper area or under the breasts
-
-
Symptoms: Itchy rash, redness, skin lesions, and irritation that may spread in just a few hours. Some fungal rashes appear raised and scaly to the naked eye.
-
Risk factors: Warm climates, tight clothing, poor hygiene, obesity, immune system suppression, or the use of topical corticosteroids/certain medications that reduce immunity.
Unlike eczema, it's contagious and can spread by touching contaminated objects, pets, or people.
Q: Is Eczema Fungal?
A: No. While they may look similar, they are different skin conditions.
-
Eczema is a chronic skin condition with genetic and environmental triggers.
-
Fungal infections are caused by fungus and spread through skin to skin contact or contaminated surfaces.
Key differences:
-
Location: Eczema can appear anywhere, while fungal infections thrive in moist areas (armpits, groin, feet, skin folds).
-
Contagious? Eczema is not contagious. Fungal infections are.
-
Treatment options: Eczema needs long-term eczema treatment strategies, while fungal infections are usually treated with antifungal creams or antifungal medications.
Q: How are Eczema and Fungal Infections Treated?
Eczema Treatment: For physician-approved, natural eczema relief, visit The Eczema Company.
-
Keep skin hydrated with emollients, balms or natural creams.
-
Avoid triggers, wear gloves when cleaning, and avoid scratching to prevent worsening lesions.
-
Gentle cleansing with a mild soap or home remedies like calamine lotion can reduce irritation.
-
In severe cases, dermatologists may recommend topical treatments like topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or antibiotic creams for secondary infections.
-
Many people find relief through holistic means like reducing stress, changing their diet and addressing the root cause of their eczema.
Fungal Infection Treatment:
-
Topical treatments like antifungal creams, powders, or sprays.
-
In persistent cases, antifungal medications may be prescribed by a dermatologist or healthcare provider.
-
Keep affected areas dry, wear breathable fabrics, and practice good hygiene to prevent reinfection.
-
Natural remedies like tea tree oil may help but should be used with caution.
Q: Can the Same Products Help Both?
Yes! Some soothing products can support eczema & fungal infections symptoms alike, especially by calming irritation and reducing infection risk.
Here are some supportive options:
-
Nourish + Hydrate Manuka Balm
With manuka honey and Lactobacillus Ferment, this balm soothes eczema flare ups, helps prevent secondary infections, and is even effective against fungus, more powerful than tea tree oil. -
Hot Skin Soother
Designed to calm oozing, red, swollen skin, this balm targets irritation in skin folds, the groin, or elbow creases. It helps manage fungal infections, eczema lesions, and even bacterial infections when treated appropriately. -
Tallow Soap Bar with Zinc
A mild soap with antifungal and antibacterial properties that gently cleanses without stripping. Great for eczema, ringworm, candida, or other skin infections. Helps prevent infection and support healthy skin tone.
Q: What to Do If You’re Unsure?
If you’re uncertain whether you’re dealing with eczema or fungal infection, the best step is to consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider. A professional exam can confirm whether you need antifungal medications, eczema treatment, or a combination of treatment options.